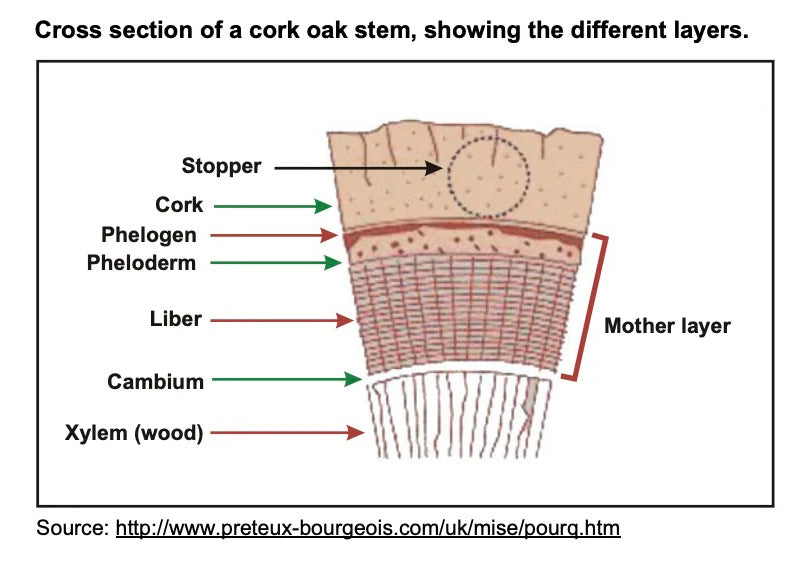
What is Cork?
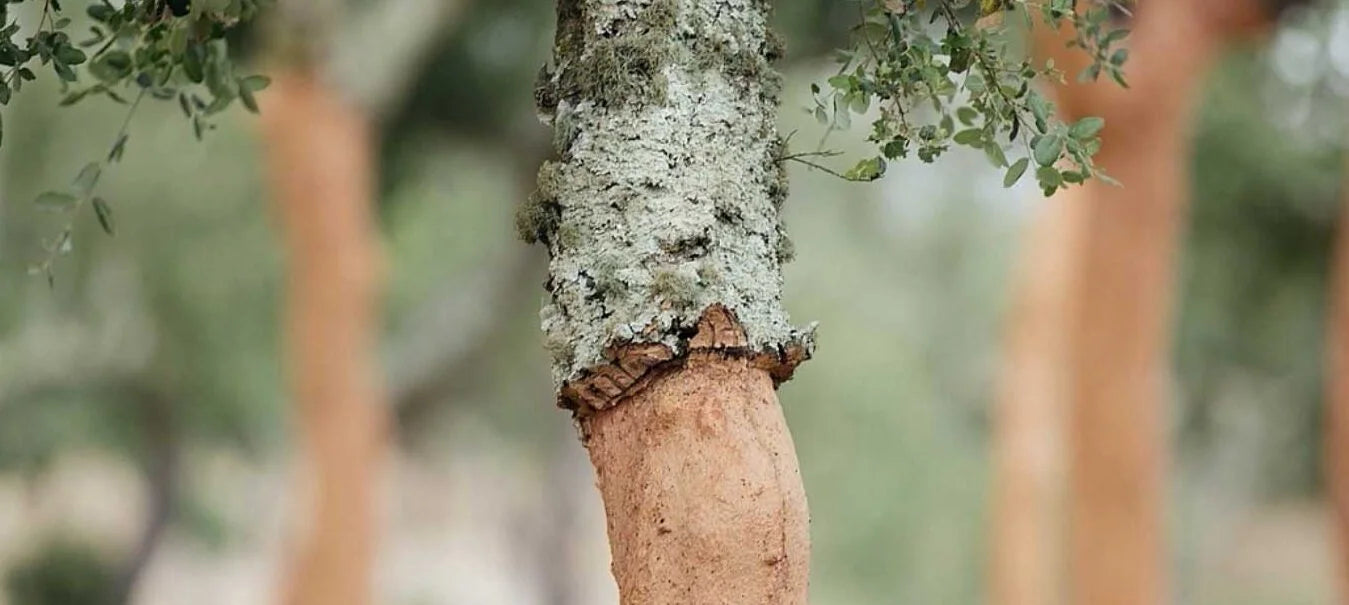
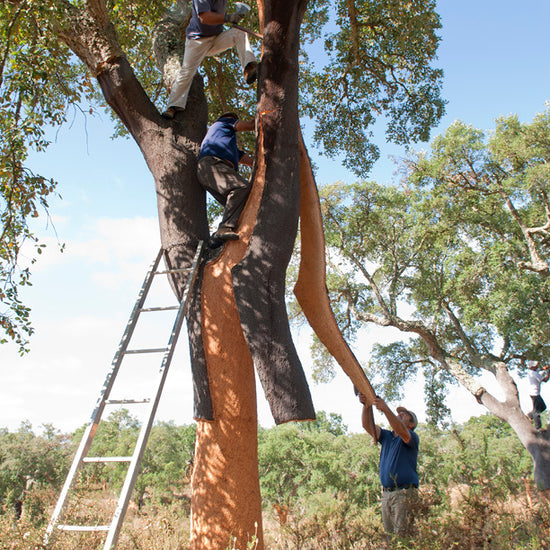
Cork comes from the harvested bark of the Quercus Suber tree. It is formed by the phelogen located in the outer bark of the cork oak. It can be easily stripped off without damaging the tree. In turn, the tree responds by regenerating new phelogen.
-
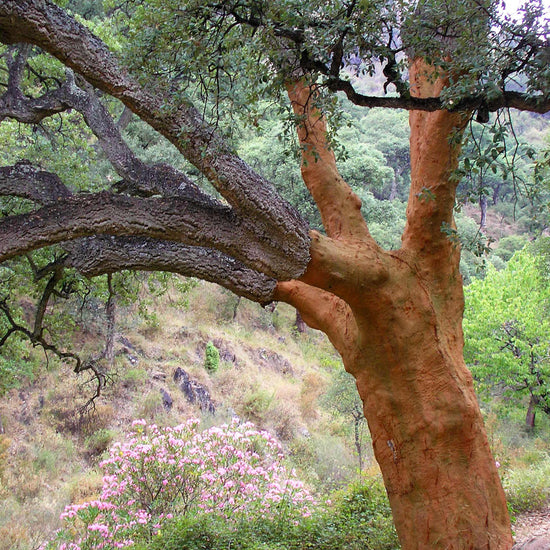

Cork trees are not cut down – they are harvested.
The first harvest happens when the tree is around 25 years old, and subsequent harvests happen every 10 years or so. the tree continues on living, unharmed.
Agreat deal of care goes into maintaining healthy trees throughout their entire lifetime. this is great for regional wildlife in and around the trees, as their natural habitat remains intact and protected. -

CO2 Absoption
As well as producing oxygen, harvested cork trees absorb 3-5 times more co2 than non-harvested trees, because each time it is harvested, cork bark regenerates itself and the trees store co2 in order to regenerate.
cork oak trees in portugal alone help offset 10 million tons of carbon every year. -

Ecological & Social Impact
The preservation of the cork oak woodlands play a key role in water retention, soil conservation and forest fire prevention.
Cork is a multi-generational and vital source of regional rural employment.. there are around 100,000 people in the iberian and mediterranean cork producing countries who are economically dependent on the industry.
Renewable, Recyclable and Biodegradable
Natural cork is an environmentally friendly material that completely biodegrades or can be readily recycled without creating any significant secondary waste.
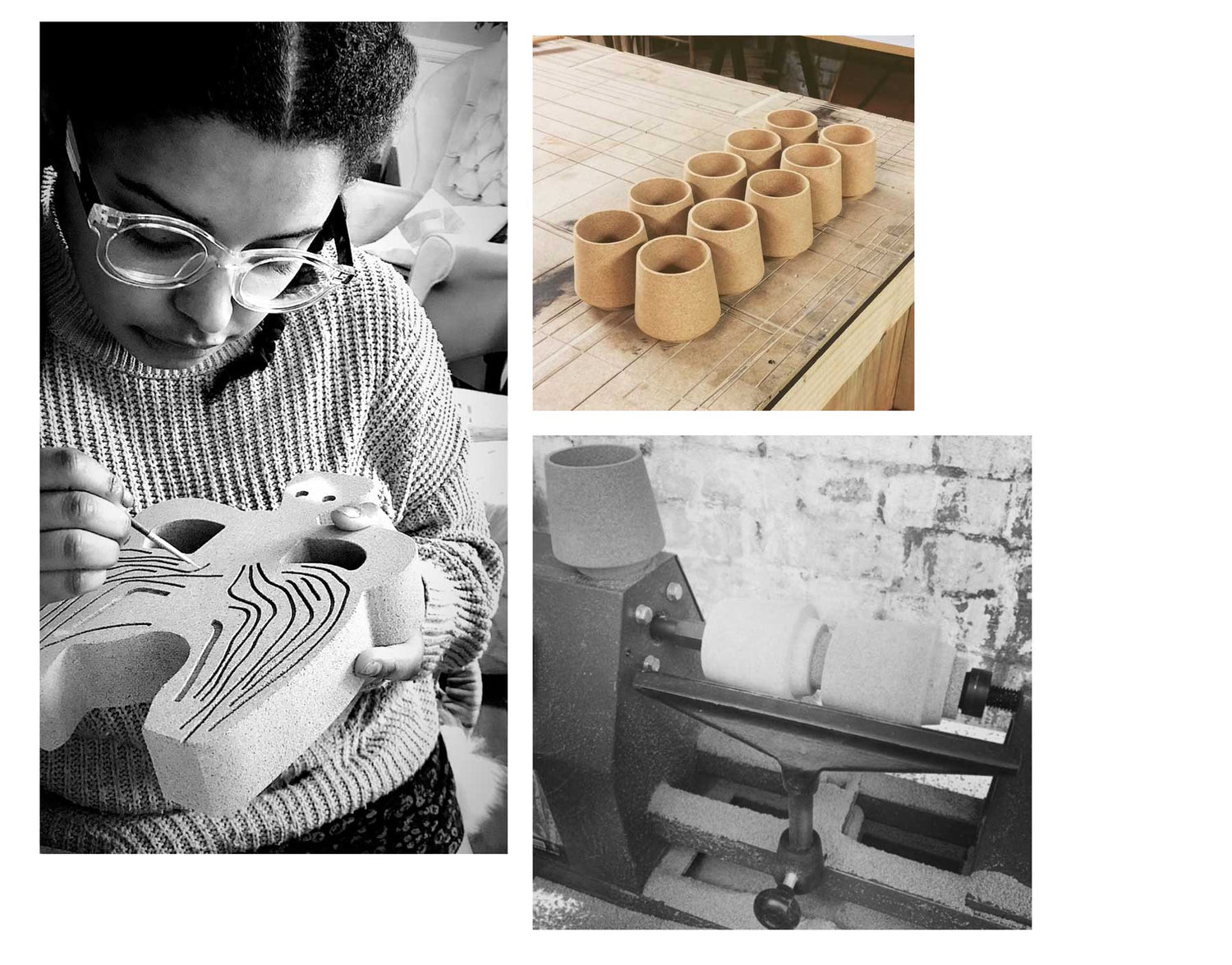

Production Processes at mind the cork
All mind the cork products are created in-house in London or with the help of craftspeople and micro-factories in the UK and Portugal.
We focus on designing to make the best of the material properties and avoiding waste, as well as repurposing and recycling any waste created during production. We use two forms of cork:
Cork agglomerate
Made of granulated cork, derived from by-products that are a result of the manufacture of natural cork closures.
Cork leather
Once the bark is removed from the tree, cork is left dry out and then steamed and boiled. That’s what gives it extra elasticity. The blocks of cork are then sliced into thin sheets and a fabric support backing is attached. The end product is a durable textile that is a beautiful cruelty-free alternative to animal leather.




